(Até a parte fácil é difícil)
Existem três formas de adicionar uma rota default na tabela BGP.
Vamos usar a topologia e as configurações abaixo, como ponto de partida, e mostrar estas opções.
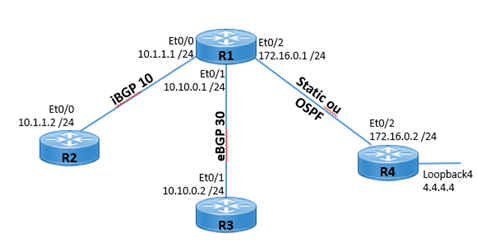
R1:
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/1
ip address 10.10.0.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/2
ip address 172.16.0.1 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 10
redistribute connected
redistribute static
neighbor 10.1.1.2 remote-as 10
neighbor 10.1.1.2 next-hop-self
neighbor 10.10.0.2 remote-as 30
!
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.0.2
ip route 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255 172.16.0.2R2:
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
!router bgp 10
redistribute connected
neighbor 10.1.1.1 remote-as 10R3:
interface Ethernet0/1
ip address 10.10.0.2 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 30
redistribute connected
neighbor 10.10.0.1 remote-as 10R4:
interface Loopback4
ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255
!
interface Loopback200
ip address 200.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
!
interface Ethernet0/2
ip address 172.16.0.2 255.255.255.0
!
ip route 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.0.1
ip route 10.10.0.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.0.1
Redistribute + Default-Information
Podemos inserir uma rota default no BGP usando os comandos redistribute e default-information originate.
Observe que no roteador R1 temos uma rota default (estática) e também o comando redistribute static já configurado (redistribuindo a outra rota estática). No entanto a rota default não está na tabela BGP dos roteadores R1, R2 e R3.
R1#sh ip route Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP a - application route + - replicated route, % - next hop override Gateway of last resort is 172.16.0.2 to network 0.0.0.0 S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 172.16.0.2 4.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets S 4.4.4.4 [1/0] via 172.16.0.2 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 4 subnets, 2 masks C 10.1.1.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0 L 10.1.1.1/32 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0 C 10.10.0.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/1 L 10.10.0.1/32 is directly connected, Ethernet0/1 172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C 172.16.0.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/2 L 172.16.0.1/32 is directly connected, Ethernet0/2 R1# R1#sh ip bgp BGP table version is 11, local router ID is 172.16.0.1 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter, x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed, Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> 4.4.4.4/32 172.16.0.2 0 32768 ? *> 10.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ? * i 10.1.1.2 0 100 0 ? *> 10.10.0.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ? * 10.10.0.2 0 0 30 ? *> 172.16.0.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ? R1# R2#sho ip bgp BGP table version is 20, local router ID is 10.1.1.2 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter, x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed, Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *>i 4.4.4.4/32 10.1.1.1 0 100 0 ? * i 10.1.1.0/24 10.1.1.1 0 100 0 ? *> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ? *>i 10.10.0.0/24 10.1.1.1 0 100 0 ? *>i 172.16.0.0/24 10.1.1.1 0 100 0 ? R2# R3#sh ip bgp BGP table version is 16, local router ID is 10.10.0.2 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter, x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed, Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> 4.4.4.4/32 10.10.0.1 0 0 10 ? *> 10.1.1.0/24 10.10.0.1 0 0 10 ? * 10.10.0.0/24 10.10.0.1 0 0 10 ? *> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ? *> 172.16.0.0/24 10.10.0.1 0 0 10 ? R3#
Vamos agora inserir o comando default-information originate para que a rota default também seja redistribuída (sem esse comando o BGP redistribui as rotas estáticas, mas não a rota default).
R1#conf t R1(config)#router bgp 10 R1(config-router)# default-information originate R1(config-router)#end R1# R1#sh ip bgp BGP table version is 12, local router ID is 172.16.0.1 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter, x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed, Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> 0.0.0.0 172.16.0.2 0 32768 ? *> 4.4.4.4/32 172.16.0.2 0 32768 ? *> 10.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ? * i 10.1.1.2 0 100 0 ? *> 10.10.0.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ? * 10.10.0.2 0 0 30 ? *> 172.16.0.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ? R1# R2#sh ip bgp BGP table version is 21, local router ID is 10.1.1.2 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter, x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed, Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *>i 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.1 0 100 0 ? *>i 4.4.4.4/32 10.1.1.1 0 100 0 ? * i 10.1.1.0/24 10.1.1.1 0 100 0 ? *> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ? *>i 10.10.0.0/24 10.1.1.1 0 100 0 ? *>i 172.16.0.0/24 10.1.1.1 0 100 0 ? R2# R3#sh ip bgp BGP table version is 17, local router ID is 10.10.0.2 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter, x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed, Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> 0.0.0.0 10.10.0.1 0 0 10 ? *> 4.4.4.4/32 10.10.0.1 0 0 10 ? *> 10.1.1.0/24 10.10.0.1 0 0 10 ? * 10.10.0.0/24 10.10.0.1 0 0 10 ? *> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ? *> 172.16.0.0/24 10.10.0.1 0 0 10 ? R3#
Também podemos redistribuir uma rota default aprendida via protocolo de roteamento, usando o mesmo conceito (redistribute + default-information).
Vamos remover a rota default do R1 e configurar OSPF entre ele e o R4 (que divulgará a rota default).
R1#conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. R1(config)#no ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.0.2 R1(config)#interface Ethernet0/2 R1(config-if)# ip ospf 40 area 0 R1(config-if)# R4#conf t R4(config)#interface Ethernet0/2 R4(config-if)# ip ospf 40 area 0 R4(config-if)#exit R4(config)#router ospf 40 R4(config-router)# default-information originate always R1#sh ip route Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP a - application route + - replicated route, % - next hop override Gateway of last resort is 172.16.0.2 to network 0.0.0.0 O*E2 0.0.0.0/0 [110/1] via 172.16.0.2, 00:00:15, Ethernet0/2 4.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets S 4.4.4.4 [1/0] via 172.16.0.2 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 4 subnets, 2 masks C 10.1.1.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0 L 10.1.1.1/32 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0 C 10.10.0.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/1 L 10.10.0.1/32 is directly connected, Ethernet0/1 172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C 172.16.0.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/2 L 172.16.0.1/32 is directly connected, Ethernet0/2 R1#
Agora que R1 tem um rota default em sua tabela de roteamento (aprendida via OSPF), basta redistribuir o OSPF no BGP.
R1#conf t R1(config)#router bgp 10 R1(config-router)#redistribute ospf 40 match external R1(config-router)#end R1#sh ip bgp BGP table version is 14, local router ID is 172.16.0.1 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter, x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed, Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> 0.0.0.0 172.16.0.2 1 32768 ? *> 4.4.4.4/32 172.16.0.2 0 32768 ? *> 10.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ? * i 10.1.1.2 0 100 0 ? *> 10.10.0.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ? * 10.10.0.2 0 0 30 ? *> 172.16.0.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ? R1# R2# sh ip bgp BGP table version is 23, local router ID is 10.1.1.2 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter, x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed, Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *>i 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.1 1 100 0 ? *>i 4.4.4.4/32 10.1.1.1 0 100 0 ? * i 10.1.1.0/24 10.1.1.1 0 100 0 ? *> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ? *>i 10.10.0.0/24 10.1.1.1 0 100 0 ? *>i 172.16.0.0/24 10.1.1.1 0 100 0 ? R2# R3#sh ip bgp BGP table version is 19, local router ID is 10.10.0.2 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter, x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed, Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> 0.0.0.0 10.10.0.1 1 0 10 ? *> 4.4.4.4/32 10.10.0.1 0 0 10 ? *> 10.1.1.0/24 10.10.0.1 0 0 10 ? * 10.10.0.0/24 10.10.0.1 0 0 10 ? *> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ? *> 172.16.0.0/24 10.10.0.1 0 0 10 ? R3#
Usando o comando network
Outra opção para divulgar uma rota default via BGP, é usando o comando network.
Utilizando nosso exemplo, vamos remover a redistribuição do OSPF e colocar o comando network 0.0.0.0.
Importante notar que para que a divulgação funcione é preciso que R1 tenha uma rota default em sua tabela de roteamento (e temos, aprendida via OSPF).
R1#conf t R1(config)#router bgp 10 R1(config-router)#no redistribute ospf 40 match external R1(config-router)#network 0.0.0.0 R1(config-router)#end R1# R1#sh ip bgp BGP table version is 16, local router ID is 172.16.0.1 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter, x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed, Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> 0.0.0.0 172.16.0.2 1 32768 i *> 4.4.4.4/32 172.16.0.2 0 32768 ? *> 10.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ? * i 10.1.1.2 0 100 0 ? *> 10.10.0.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ? * 10.10.0.2 0 0 30 ? *> 172.16.0.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ? R1# R2#sh ip bgp BGP table version is 25, local router ID is 10.1.1.2 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter, x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed, Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *>i 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.1 1 100 0 i *>i 4.4.4.4/32 10.1.1.1 0 100 0 ? * i 10.1.1.0/24 10.1.1.1 0 100 0 ? *> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ? *>i 10.10.0.0/24 10.1.1.1 0 100 0 ? *>i 172.16.0.0/24 10.1.1.1 0 100 0 ? R2# R3#sh ip bgp BGP table version is 21, local router ID is 10.10.0.2 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter, x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed, Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> 0.0.0.0 10.10.0.1 1 0 10 i *> 4.4.4.4/32 10.10.0.1 0 0 10 ? *> 10.1.1.0/24 10.10.0.1 0 0 10 ? * 10.10.0.0/24 10.10.0.1 0 0 10 ? *> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ? *> 172.16.0.0/24 10.10.0.1 0 0 10 ? R3#
Neighbor default-originate
Por fim, podemos anunciar uma rota default via BGP usando o comando neighbor x.x.x.x default-originate.
Neste caso o roteador anuncia a rota default para o neighbor especificado, mas não insere a rota default na tabela de roteamento local.
Quando usamos este comando o roteador faz o anuncio da rota default sem verificar se ele tem uma rota default em sua tabela de roteamento, mas essa verificação pode ser configurada usando route-map.
R1#conf t R1(config)#int et0/2 R1(config-if)#no ip ospf 40 area 0 R1(config-if)#exit R1(config)#router bgp 10 R1(config-router)#no network 0.0.0.0 R1(config-router)#no default-information originate R1(config-router)#neighbor 10.1.1.2 default-originate R1(config-router)#end R1# R1#sh ip bgp BGP table version is 18, local router ID is 172.16.0.1 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter, x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed, Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0 i *> 4.4.4.4/32 172.16.0.2 0 32768 ? *> 10.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ? * i 10.1.1.2 0 100 0 ? *> 10.10.0.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ? * 10.10.0.2 0 0 30 ? *> 172.16.0.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ? R1#sh ip route 0.0.0.0 % Network not in table R1# R2#sh ip bgp BGP table version is 27, local router ID is 10.1.1.2 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter, x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed, Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *>i 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.1 0 100 0 i *>i 4.4.4.4/32 10.1.1.1 0 100 0 ? * i 10.1.1.0/24 10.1.1.1 0 100 0 ? *> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ? *>i 10.10.0.0/24 10.1.1.1 0 100 0 ? *>i 172.16.0.0/24 10.1.1.1 0 100 0 ? R2# R3#sh ip bgp BGP table version is 22, local router ID is 10.10.0.2 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter, x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed, Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> 4.4.4.4/32 10.10.0.1 0 0 10 ? *> 10.1.1.0/24 10.10.0.1 0 0 10 ? * 10.10.0.0/24 10.10.0.1 0 0 10 ? *> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ? *> 172.16.0.0/24 10.10.0.1 0 0 10 ? R3#
OBS: Em alguns documentos fala que quando usamos o comando neighbor x.x.x.x default-originate o roteador não insere a rota default na tabela BGP local. O que vi (usando o UNL) é que a rota é sim inserida na tabela BGP, mas ela não é a best route. Acredito que essa mudança no comportamento se deve a versão do IOS (ou talvez por conta do simulador).
Até a próxima.



